Matlab: Dijkstra Methode - große Nachbarschaft
Die Dijkstra Methode
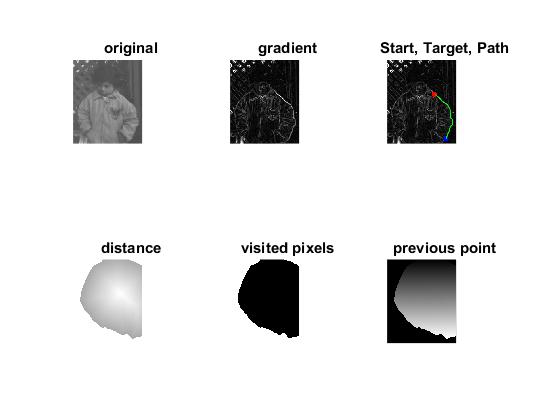
(English) In diesem Post wird die Dijkstra Methode aus dem vorherigen Post nochmal aufgearbeitet, sodass diese eine größere Nachbarschaft nach Wegen durchsucht und somit bei mehreren möglichen Pfäden eine präziesere Lösung findet.Die wird in folgendem Bild zu dme vorherigen Post verglichen:
Quellcode Dijkstra:
function [path, prev, unvis, distance, start, target] = Dijkstra_Methode(Matrix, start, target)%Matrix is the incoming image
%start is the start point in a vector [a,b] where a is the column and b the
%row
%target is the end point similare to start
%path is the matrix with ones excepted at the position of the path where it is 0
%prev are also the previous visited pixels where the algorithm took the
%wrong way
%unvis are all unvisited pixels
%distance is the distance or weight of the pixels
%open the image and you can choose with the cursor the start
%and end point if you don't give the function these values
if nargin == 1
fig(1) = figure(1);
clf(1);
imshow(Matrix);
dcm_obj = datacursormode(fig(1));
set(dcm_obj,'DisplayStyle','datatip','SnapToDataVertex','off','Enable','on')
disp('Click for start point')
pause
pos1 = getCursorInfo(dcm_obj);
pos = pos1.Position;
sx1 = pos(2);
sy1 = pos(1);
start = [sx1 sy1];
disp('Click for end point')
pause
pos2 = getCursorInfo(dcm_obj);
pos = pos2.Position;
sx2 = pos(2);
sy2 = pos(1);
target = [sx2 sy2];
end
%calculate amount of nodes
n = size(Matrix);
vis = zeros(n);
unvis = ones(n); %set all unvisited to 1
distance = ones(n).*inf; %set all distances to inf
prev = zeros(n);%previous node
prev1 = zeros(n);%previous node
prev2 = zeros(n);%previous node
Q = zeros(n);
for i=1:1:n(1)
for j=1:1:n(2)
Q(i,j) = (j-1)*n(1)+i;
end
end
%strt = (start(1)-1)*n(1)+start(2);
%trgt = (target(1)-1)*n(1)+target(2);
u = start;
distance(u(1),u(2)) = 0;%startdistance is 0
while max(Q) ~= 0
test = inf;
for i = 1:1:n(1)
for j = 1:1:n(2)
if Q(i,j)~=0 && distance(i,j)<test
test = distance(i,j);
u = [i j];
end
end
end
%if i is in Q
Q(u(1),u(2)) = 0;
%end
vis(u) = 1;
%if etime(clock,starttime) > inf %safety time stop
%break
%end
for i=1:1:3
for j=1:1:3
if(i==2 && j ==2)
continue
end
%v=u-2+i+sz*(j-2);
vx = u(1)-2+i;
vy = u(2)-2+j;
v = [vx vy];
if vx <= 0 || vy <= 0 || vx >= n(1) || vy >= n(2)
continue
end
if Q(vx,vy) == 0
continue
end
cost = distance(u(1),u(2))+localedgewidth(Matrix,u,v);
if (cost<distance(vx,vy))
distance(vx,vy)=cost;
prev(vx,vy)=(u(1)-1)*n(2)+u(2);
prev1(vx,vy) = u(1);
prev2(vx,vy) = u(2);
end
end
end
unvis(u(1),u(2))=0;
if (u(1) == target(1) && u(2) == target(2))
break
end
end
distance(distance==inf) = 0;
distance = distance./255;
path=zeros(n);
path(u) = 1;
%u = target;
%backtrack from end to start to find best sequence
while u ~= start
v = u;
u(1) = prev1(v(1),v(2));
u(2) = prev2(v(1),v(2));
path(u(1),u(2)) = 1;
end
end
function [weight] = localedgewidth(G,p,q)
maxG=max(G(:));
minG=min(G(:));
%d=sqrt(sum((p-q).^2));
d = [sqrt(2) 1 sqrt(2); 1 0 1; sqrt(2) 1 sqrt(2)];
i = 2+(q(1)-p(1));
j = 2+(q(2)-p(2));
weight=(maxG-G(q(1),q(2)))/(maxG-minG) *d(i,j)/sqrt(2);
end


Kommentare
Kommentar veröffentlichen